Apple Messages for Business
[ˈæpəl ˈmɛsɪdʒɪz fɔr ˈbɪznɪs]Apple Messages for Business is a platform that connects businesses with customers through the Messages app on iOS devices. It supports inquiries, support, appointments, and Apple Pay transactions in a secure environment. This service enhances customer experiences with familiar iMessage tools.
Why Apple Messages for Business Matters
Apple Messages for Business bridges companies and iOS users directly in a preferred app, elevating support quality and satisfaction.
By enabling real-time, multimedia interactions, it reduces reliance on calls or emails, leading to faster resolutions and lower operational costs. Businesses see uplifts in loyalty as customers appreciate convenient features like in-app payments.
It also captures valuable interaction data for insights, refining services and personalizing future engagements.
In omnichannel strategies, it integrates seamlessly, ensuring consistent experiences across touchpoints. With Apple’s vast user base, adopting this channel expands reach, driving conversions and retention in competitive markets.
How Apple Messages for Business Works
Apple Messages for Business operates via integrations that route customer-initiated chats to business systems.
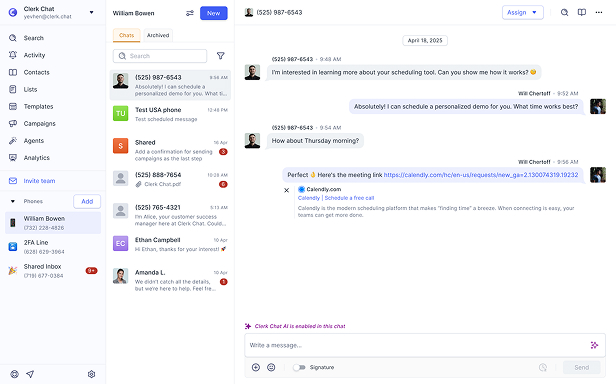
Customer Initiation: Users start conversations from Maps, Safari, Siri, Search, or business apps/websites by tapping a Message button.
Routing to MSP: Messages go through an approved Messaging Service Provider (MSP) that handles encryption and delivery to the business’s backend.
Agent Response: Businesses use integrated tools like Zendesk or Salesforce to receive and reply, supporting live agents or bots for initial triage.
Feature Utilization: Incorporate rich elements such as images, videos, calendars for scheduling, or Apple Pay for transactions within the chat.
Trigger Handling: Respond to standardized words like “agent” for escalation, “menu” for options, or “unsubscribe” for preferences.
Privacy and Deletion: Messages are encrypted; if customers delete threads, businesses cannot reinitiate contact until the user does.
Analytics and Closure: Track metrics via the MSP dashboard; conversations end naturally or via opt-out.
In practice, a customer queries a product via Siri, receives images and a payment link, completes a purchase - all encrypted and within Messages. This setup requires Apple approval, ensuring compliance and quality.
Best Practices with Apple Messages for Business
Prioritize Customer Initiation: Design entry points in apps and sites to encourage starts, respecting no-unsolicited rule.
Integrate Rich Features: Use multimedia, Apple Pay, and scheduling to enrich interactions, boosting completion rates.
Staff Adequately for Live Support: Forecast needs with tools to maintain response times comparable to phone.
Handle Triggers Efficiently: Program responses for words like “agent” or “unsubscribe” to streamline flows.
Ensure Data Privacy: Encrypt all exchanges and honor deletions to comply and build trust.
Automate Where Possible: Deploy bots for FAQs, escalating to humans for complex issues.
Monitor and Refine: Analyze CSAT and engagement to optimize content and workflows.
Real world examples
- Customer Service
Teams resolve queries via Messages, cutting response times by 40%.
Read more - Logistics
Firms update deliveries in-app, enhancing tracking accuracy by 30%.
Read more
Common misconceptions
Only customers can start chats; businesses respond but cannot send unsolicited messages.
It connects with platforms like Zendesk and Salesforce for unified workflows.
It supports images, videos, Apple Pay, and calendars for rich interactions.
Strict guidelines on consent, privacy, and messaging must be followed to avoid violations.
Related terms
In this article:
Ready to use your business number for text messaging?
Thousands of businesses are already experiencing the power of conversational messaging through SMS. Join us. Free trial and paid tiers available.
Get StartedFAQ
Have questions? We've got answers.
Find what you need quickly and clearly with our most frequently asked questions.
Apple Messages for Business lets companies communicate with customers through the Messages app on Apple devices. Uses include answering questions, providing support, scheduling appointments, and facilitating payments via Apple Pay. It leverages familiar iMessage features like emojis and rich links, achieving high engagement with secure, encrypted interactions.
Partner with an approved Messaging Service Provider (MSP) for configuration and integration. Submit for Apple review twice: post-setup and pre-launch. Integrate with CRMs or support tools. Ensure agents handle live chats during business hours. Platforms like Clerk Chat can complement by managing multi-channel messaging, including potential Apple integrations.
Costs vary by MSP, often including setup fees and per-message charges around $0.01-0.05. Resources involve developer time for integrations (weeks) and agent training. Benefits like 35% higher CSAT offset expenses, with ROI from reduced calls and efficient support.
Unlike SMS's text limits, it offers rich media and Apple Pay within iOS. RCS adds features to Android messaging but lacks Apple's ecosystem integration. It's ideal for Apple users, providing end-to-end encryption superior to standard SMS, though SMS ensures cross-platform reach.
Prohibit unsolicited messages; customers initiate. Provide live agents comparable to phone support. Use trigger words like 'agent' for escalations. Honor unsubscribes promptly. Protect privacy with encryption; do not share data without consent. Violations risk channel suspension.
Automate FAQs with bots but ensure human availability. Personalize with customer data from integrations. Monitor metrics like resolution time. Offer features like scheduling and payments. Train agents on guidelines to maintain compliance and quality interactions.