Chatbot
[ˈtʃætˌbɒt]A chatbot is a computer program that simulates human conversation through text chats or voice commands, enabling automated interactions with users.
It processes inputs and generates responses based on predefined rules or artificial intelligence. This technology supports various applications, from customer service to information retrieval.
Why Chatbot Matters
Chatbots enhance customer experiences by delivering instant responses, available 24/7, which significantly reduces wait times and boosts satisfaction levels.
In business contexts, they handle high volumes of inquiries efficiently, allowing human agents to focus on intricate issues, thereby optimizing operational costs. This leads to measurable outcomes like decreased resolution times and increased retention rates.
They also collect interaction data, providing insights into user preferences and behaviors that inform product development and marketing tactics.
As digital engagement grows, chatbots facilitate seamless multichannel support, strengthening brand loyalty. Overall, their adoption correlates with improved efficiency, with some organizations achieving 30-40% reductions in support expenses.
How Chatbot Works
Chatbots process user interactions through a series of steps, varying by type.
Input Reception: The chatbot receives user queries via text from messaging platforms or voice through integrated systems, often converting speech to text.
Input Analysis: For rule-based chatbots, it matches keywords or patterns to predefined rules; AI-based ones use natural language processing to understand intent and context.
Response Generation: It selects or generates a reply from scripts, databases, or machine learning models, ensuring relevance.
Output Delivery: The response is sent back in the original format, maintaining conversation flow.
Session Management: Tracks dialogue history to provide context-aware responses in multi-turn exchanges.
Learning (for AI types): Analyzes interactions post-session to improve future accuracy through feedback loops.
In practical use, a customer might ask about order status via text, prompting the chatbot to query a backend system and respond accordingly.
Best Practices with Chatbot
Define Clear Objectives: Specify use cases like FAQ handling or lead capture to guide design and measure success effectively.
Handle Ambiguities Gracefully: Prepare for unclear inputs by offering clarifications or options, preventing frustration.
Enable Easy Escalation: Allow seamless handover to human agents when limits are reached, maintaining service quality.
Test Extensively: Simulate diverse scenarios, including edge cases, to refine accuracy and user experience.
Personalize Responses: Use available data to tailor replies, increasing engagement and perceived value.
Monitor Performance Metrics: Track resolution rates and feedback to iterate and optimize continuously.
Ensure Accessibility: Design for inclusivity, supporting multiple languages and voice for broader reach.
Real world examples
- Customer Service
Support teams use chatbots for initial triage, resolving 70% of common queries instantly.
Read more - Education
Schools deploy chatbots for student FAQs, increasing response speed by 40%.
Read more
Common misconceptions
Many chatbots rely on rule-based systems with predefined scripts, not AI, limiting them to simple interactions.
They excel at routine queries but often need human escalation for complex or empathetic situations.
Effective chatbots require careful planning, testing, and iteration to handle diverse user inputs accurately.
Related terms
In this article:
Ready to use your business number for text messaging?
Thousands of businesses are already experiencing the power of conversational messaging through SMS. Join us. Free trial and paid tiers available.
Get StartedFAQ
Have questions? We've got answers.
Find what you need quickly and clearly with our most frequently asked questions.
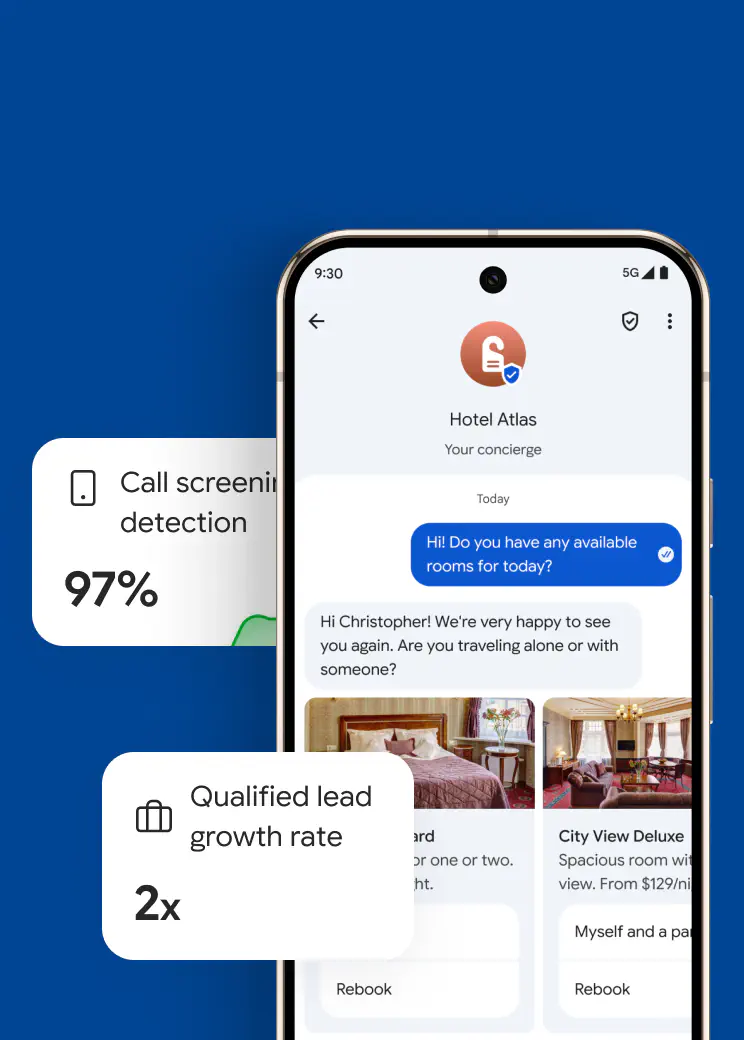
A chatbot is a program designed to mimic human conversation through text or voice interfaces. It functions in customer support for query handling, in sales for lead generation, and in internal tools for information retrieval. With open rates near 98% in messaging, chatbots provide quick responses, scaling interactions without additional staffing.
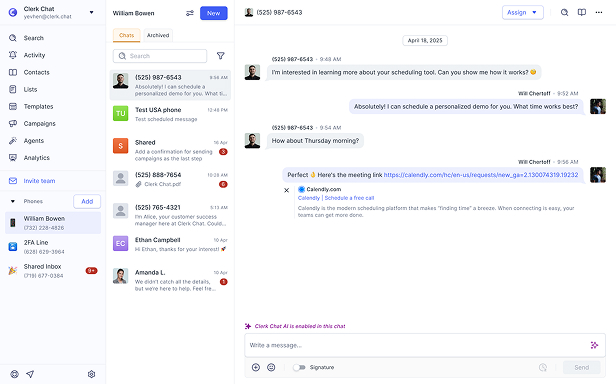
Choose a platform supporting rule-based or AI models, define conversation flows, and train on relevant data. Integrate via APIs into websites, apps, or messaging channels. Test with user scenarios for accuracy. Advanced platforms like Clerk Chat extend beyond basic chatbots by incorporating AI agents for tasks such as follow-ups and integrations, offering a more comprehensive solution.
Basic chatbots start at $20-100/month, with AI versions at $200+, plus per-message fees of $0.001-0.01. Resources include design time (days to weeks) and ongoing maintenance. ROI manifests through 30-50% reduction in support tickets, making it cost-effective for high-volume operations.
Traditional chatbots use fixed rules for responses, while conversational AI employs NLP for natural dialogues, and AI agents act autonomously on goals. Chatbots suit simple tasks; advanced systems handle complexity better. For instance, Clerk Chat utilizes AI agents rather than basic chatbots, enabling proactive features like lead qualification, distinguishing it as a broader messaging platform.
Adhere to GDPR for data protection and TCPA for consent in communications. Include opt-in/out mechanisms and secure data storage. Monitor for biases in AI models. In regions like the US, register for 10DLC to ensure deliverability. Non-adherence can result in fines, so use audit-ready logs.
Design intuitive flows with quick replies and escalation options. Train on diverse datasets for better understanding. Personalize based on user history. Analyze interactions to refine responses. Keep conversations concise and provide clear guidance on capabilities to set expectations.