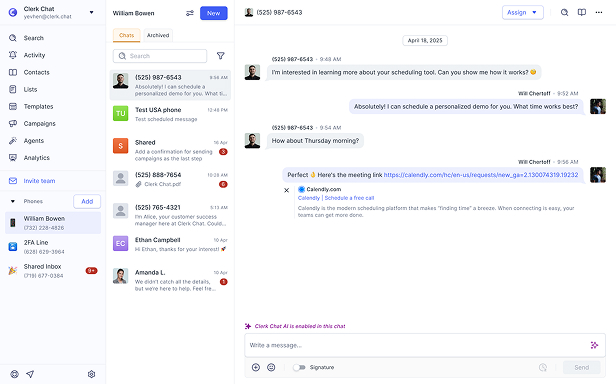
SMS Gateway
[ɛs ɛm ɛs ˈɡeɪtˌweɪ]An SMS Gateway is a software platform that facilitates the sending and receiving of text messages between applications and telecom networks. It translates data formats to ensure compatibility, allowing businesses to communicate via SMS or MMS without direct carrier integrations.
This enables scalable messaging for customer outreach and operations.
Why SMS Gateway Matters
SMS Gateways play a central part in enabling direct, immediate communication channels that outperform email in reach and response, with texts read within minutes by most recipients. In business communications, they support critical functions like alerts and verifications, which build customer trust and loyalty. For instance, they allow sending of time-sensitive information, leading to reduced no-show rates in appointments or faster resolution in support queries, directly contributing to operational efficiency.
Beyond basics, SMS Gateways impact customer engagement by personalizing interactions at scale, fostering stronger relationships and higher conversion rates in marketing efforts.
They also provide redundancy against network issues, ensuring message delivery, which is vital for global operations. Ultimately, adopting an SMS Gateway can yield significant returns, such as cost savings from automated processes and increased revenue from engaged audiences, making it indispensable for competitive edges in customer-facing sectors.
How SMS Gateway Works
An SMS Gateway operates as a bridge, handling the technical translation and routing of messages.
Message Creation: The sender composes a text in an application, such as a CRM or custom software.
API Submission: The application submits the message to the SMS Gateway via an API, like HTTP or SMPP, including recipient numbers and content.
Format Conversion: The gateway converts the message into a protocol understood by mobile carriers, such as transforming web data into SMS-compatible signals.
Routing to Carriers: It identifies the recipient’s network and routes the message through aggregators or direct connections to the carrier’s Short Message Service Center (SMSC).
Delivery to Device: The carrier forwards the SMS to the mobile device, where it’s received as a standard text.
Receipt Confirmation: The gateway captures delivery reports from the carrier and sends them back to the originating application for tracking.
Inbound Handling: For replies, the process reverses: the gateway receives the SMS from the carrier, converts it, and delivers it to the application via webhook or API.
This workflow supports bulk operations and two-way communication, with modern gateways offering cloud scalability for high volumes without latency. In context, businesses integrate gateways to automate flows, like triggering notifications from events in their systems.
Best Practices with SMS Gateway
Prioritize Reliable Providers: Select gateways with high uptime (99.99%) and global carrier connections to minimize delivery failures and support international messaging.
Implement API Security: Use HTTPS and authentication tokens in API calls to protect sensitive data during transmission and prevent unauthorized access.
Monitor Delivery Metrics: Track rates of delivery, failures, and responses via the gateway’s dashboard to identify and resolve issues like carrier blocks promptly.
Obtain Explicit Consent: Always secure user opt-in before sending, including clear opt-out instructions in messages to comply with laws and maintain list quality.
Optimize Message Content: Keep texts concise, under 160 characters, and test for character encoding to avoid segmentation that could increase costs or confuse recipients.
Use Failover Mechanisms: Configure multiple routes or backup providers within the gateway to reroute messages automatically if primary paths fail.
Integrate with Analytics: Link the gateway to tools for A/B testing and performance analysis, refining campaigns based on engagement data for better outcomes.
Real world examples
- Healthcare
Clinics send appointment reminders via SMS Gateways, cutting no-shows by 25% and improving patient flow.
Read more - Retail
Stores dispatch promotional alerts through SMS Gateways, boosting in-store traffic by 15%.
Read more
Common misconceptions
Modern SMS Gateways are primarily software-based and cloud-hosted, requiring no dedicated hardware beyond standard computing resources.
They scale effectively for businesses of all sizes, with affordable plans available for small operations.
Many advanced SMS Gateways handle MMS, allowing images, videos, and other media alongside text.
Reputable providers include built-in tools for consent management and regulatory adherence, simplifying compliance.
Related terms
In this article:
Ready to use your business number for text messaging?
Thousands of businesses are already experiencing the power of conversational messaging through SMS. Join us. Free trial and paid tiers available.
Get StartedFAQ
Have questions? We've got answers.
Find what you need quickly and clearly with our most frequently asked questions.
An SMS Gateway serves as an intermediary that converts messages from applications into formats compatible with mobile networks, facilitating SMS transmission and reception. Businesses use it for reliable, scalable to high volumes, text communication, which boasts open rates over 90%. It integrates with APIs, supporting features like automation, making it ideal for notifications, alerts, and customer interactions without needing direct carrier connections.
Start by selecting a provider offering API access. Sign up for an account, obtain API credentials, and connect your application using HTTP or SMPP. Test with sample messages to verify delivery, then integrate into workflows. Providers often supply SDKs for languages like Python or Java, along with dashboards for monitoring. For platforms like Clerk Chat, setup involves linking existing numbers for immediate use.
Costs include per-message fees, typically $0.005-$0.01 per SMS, plus monthly subscriptions starting at $10-50 for basic tiers. Resources needed are minimal: developer time for integration (a few hours) and computing for API calls. Higher volumes unlock discounts, and some offer pay-as-you-go models. Factor in potential carrier fees for numbers or compliance tools to avoid hidden expenses.
Unlike direct carrier APIs, which limit to specific networks, SMS Gateways aggregate multiple for global reach and redundancy. Email-to-SMS is simpler but less reliable, lacking delivery reports and two-way support. Gateways provide analytics, higher deliverability, and features like MMS, making them for professional use, though with added abstraction layer versus direct's potential cost savings in niche cases.
Key regulations like TCPA and GDPR require opt-in consent, message limits, and opt-out options. Gateways must log interactions for audits and filter spam. Providers assist with 10DLC registration for US businesses to maintain trust. Always include sender identification and monitor complaint rates to stay compliant, preventing blocks or fines up to $1,000 per violation.
Segment audiences for targeted messaging to increase relevance. Use short, clear content under 160 characters. Schedule sends during business hours. Monitor metrics like delivery and response rates to adjust strategies. Implement failover routes for reliability. Leverage APIs for automation, and regularly clean contact lists to maintain high engagement and low bounce rates.